Streaming IoT Data to Snowflake with EMQX 6.0 Connector

Table of Contents
The Internet of Things (IoT) generates a relentless stream of data. The challenge? Getting that data from millions of devices into your cloud data warehouse in real time. Batch processing and complex ETL pipelines are too slow, leaving your insights hours or even days behind.
What if you could stream data directly from your MQTT broker into Snowflake, ready for analysis in seconds?
With the new Snowflake Streaming integration in EMQX 6.0, this is now a simple, out-of-the-box reality. This guide will show you how to build a high-throughput, real-time data bridge that seamlessly connects your IoT devices to Snowflake.
Prerequisites
Before you begin, ensure you have the following ready:
An active Snowflake account.
EMQX 6.0 Enterprise Edition downloaded and installed.
A public and private RSA key pair. You can generate this using OpenSSL:
# Generate private key openssl genrsa 2048 | openssl pkcs8-topk8-inform PEM -out snowflake_rsa_key.private.pem-nocrypt # Generate public key openssl rsa -in snowflake_rsa_key.private.pem -pubout -out snowflake_rsa_key.public.pem
Part 1: Prepare Your Snowflake Environment
First, let's get Snowflake ready to receive the high-speed data stream. We'll create the necessary database, table, and a streaming pipe.
Step 1. Create the Database, Table, and Pipe
Log in to your Snowflake worksheet and execute the following SQL. We'll create a database (testdatabase), a target table (emqx), and the CREATE PIPE command that enables streaming ingestion. This pipe is the high-speed on-ramp for your MQTT data.
USE ROLE accountadmin;
-- Create a database to store your data
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS testdatabase;
-- Create a table to receive MQTT data
CREATE OR REPLACE TABLE testdatabase.public.emqx (
clientid STRING,
topic STRING,
payload STRING,
publish_received_at TIMESTAMP_LTZ
);
-- Create a pipe for streaming mode (direct ingestion)
CREATE PIPE IF NOT EXISTS testdatabase.public.emqxstreaming
AS
COPY INTO testdatabase.public.emqx (clientid, topic, payload, publish_received_at)
FROM (
SELECT
$1:clientid::STRING,
$1:topic::STRING,
$1:payload::STRING,
$1:publish_received_at::TIMESTAMP_LTZ
FROM TABLE(DATA_SOURCE(TYPE => 'STREAMING'))
);
Step 2. Create a Dedicated User and Role
For security and best practices, we'll create a dedicated user (snowpipeuser) and role (snowpipe) with the minimum permissions required for streaming.
-- Create a role for streaming
CREATE OR REPLACE ROLE snowpipe;
-- Grant the necessary privileges to the role
GRANT USAGE ON DATABASE testdatabase TO ROLE snowpipe;
GRANT USAGE ON SCHEMA testdatabase.public TO ROLE snowpipe;
GRANT INSERT, SELECT ON testdatabase.public.emqx TO ROLE snowpipe;
GRANT OPERATE, MONITOR ON PIPE testdatabase.public.emqxstreaming TO ROLE snowpipe;
-- Create a user for EMQX
CREATE USER IF NOT EXISTS snowpipeuser;
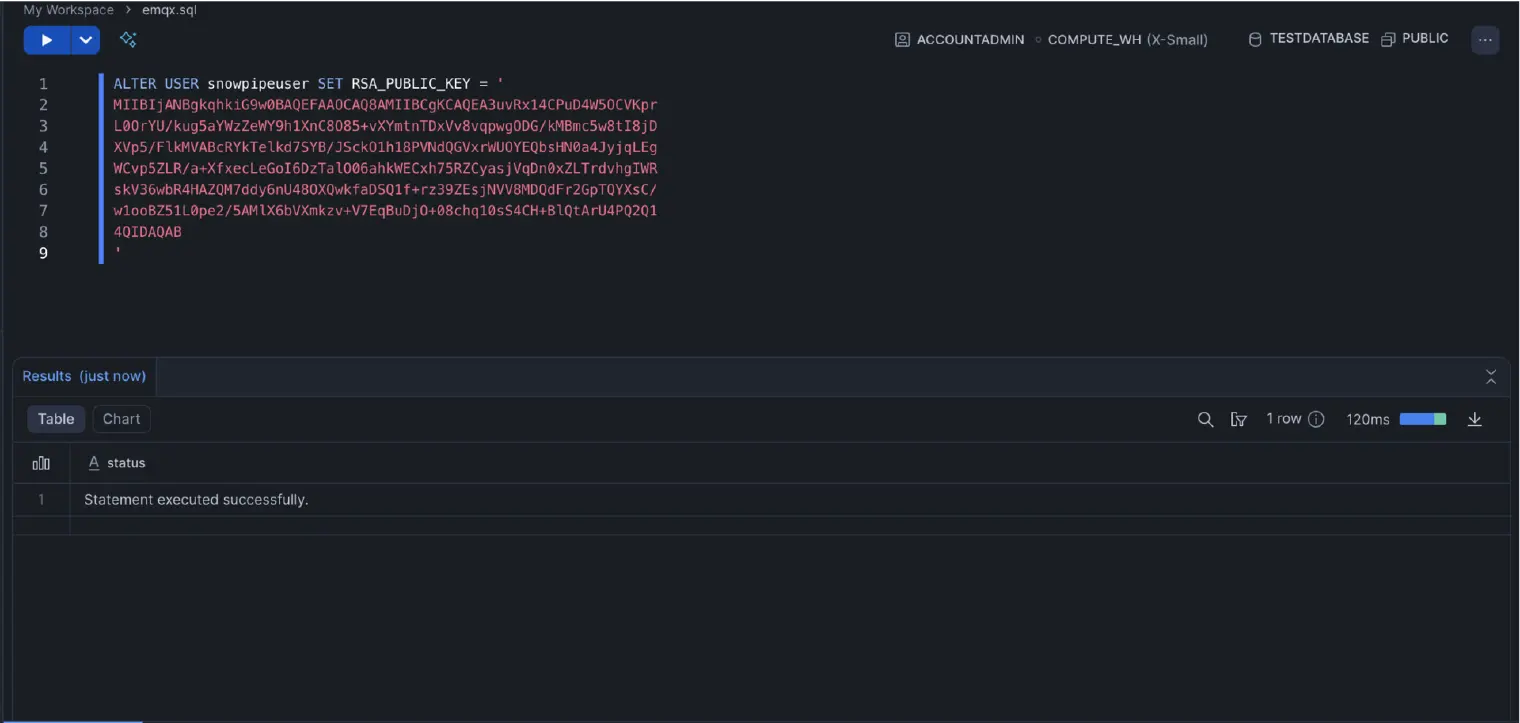
When assigning the public key, you need to format it correctly. You must remove the -----BEGIN PUBLIC KEY----- and -----END PUBLIC KEY----- lines from the PEM file, and include the remaining content, preserving any line breaks.
-- Assign the formatted public key to the user
ALTER USER snowpipeuser SET RSA_PUBLIC_KEY = '
...YOUR_FORMATTED_PUBLIC_KEY...
';
-- Grant the role to the user and set it as default
GRANT ROLE snowpipe TO USER snowpipeuser;
ALTER USER snowpipeuser SET DEFAULT_ROLE = snowpipe;
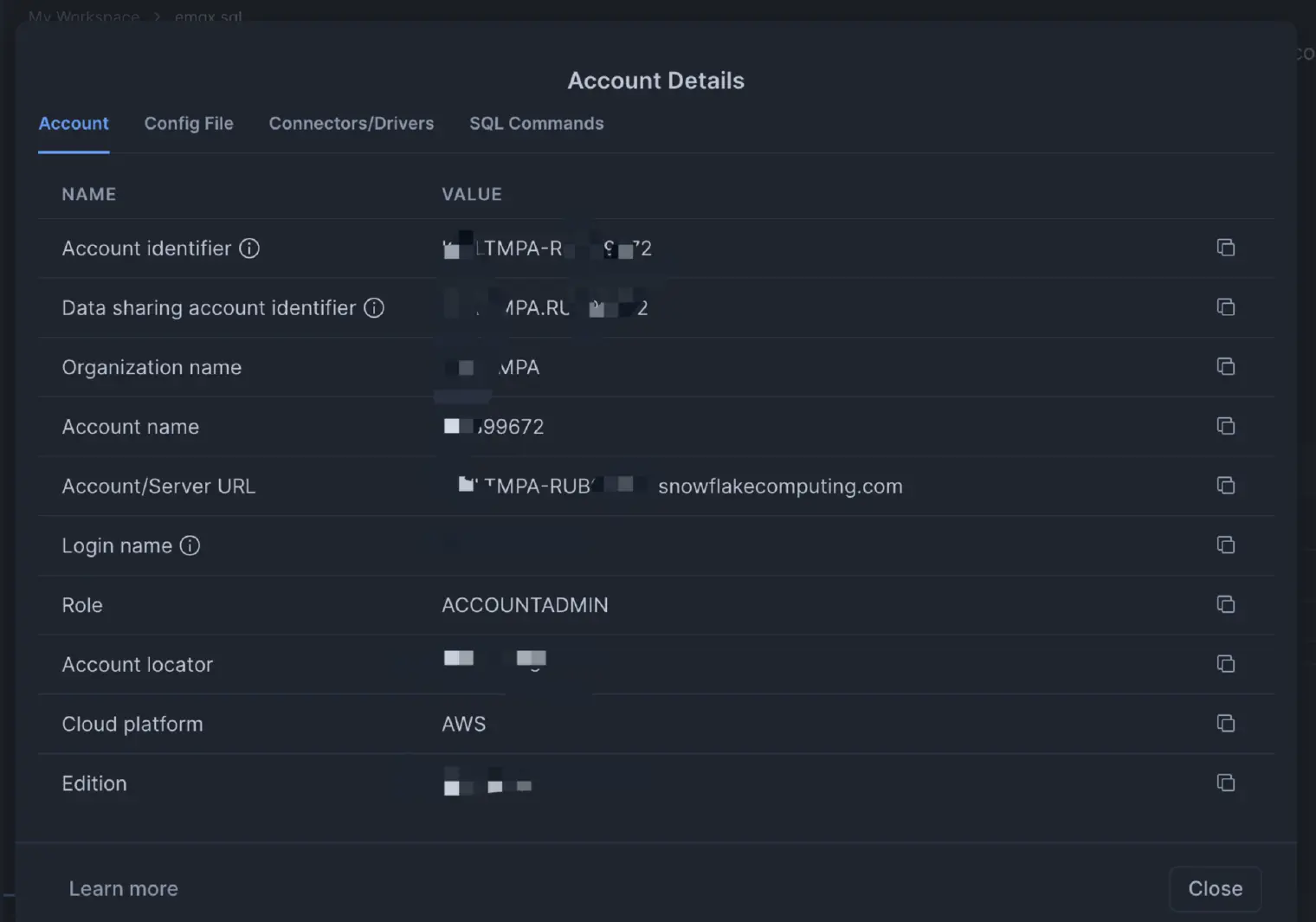
Step 3. Get Your Account Details
Finally, locate your Snowflake account URL and identifier. You'll need these to configure EMQX.
Part 2: Configure the EMQX Data Integration
Now for the easy part. Let's head over to the EMQX Dashboard to configure the integration. This is all done through the UI—no code required.
Step 1. Create the Snowflake Streaming Connector
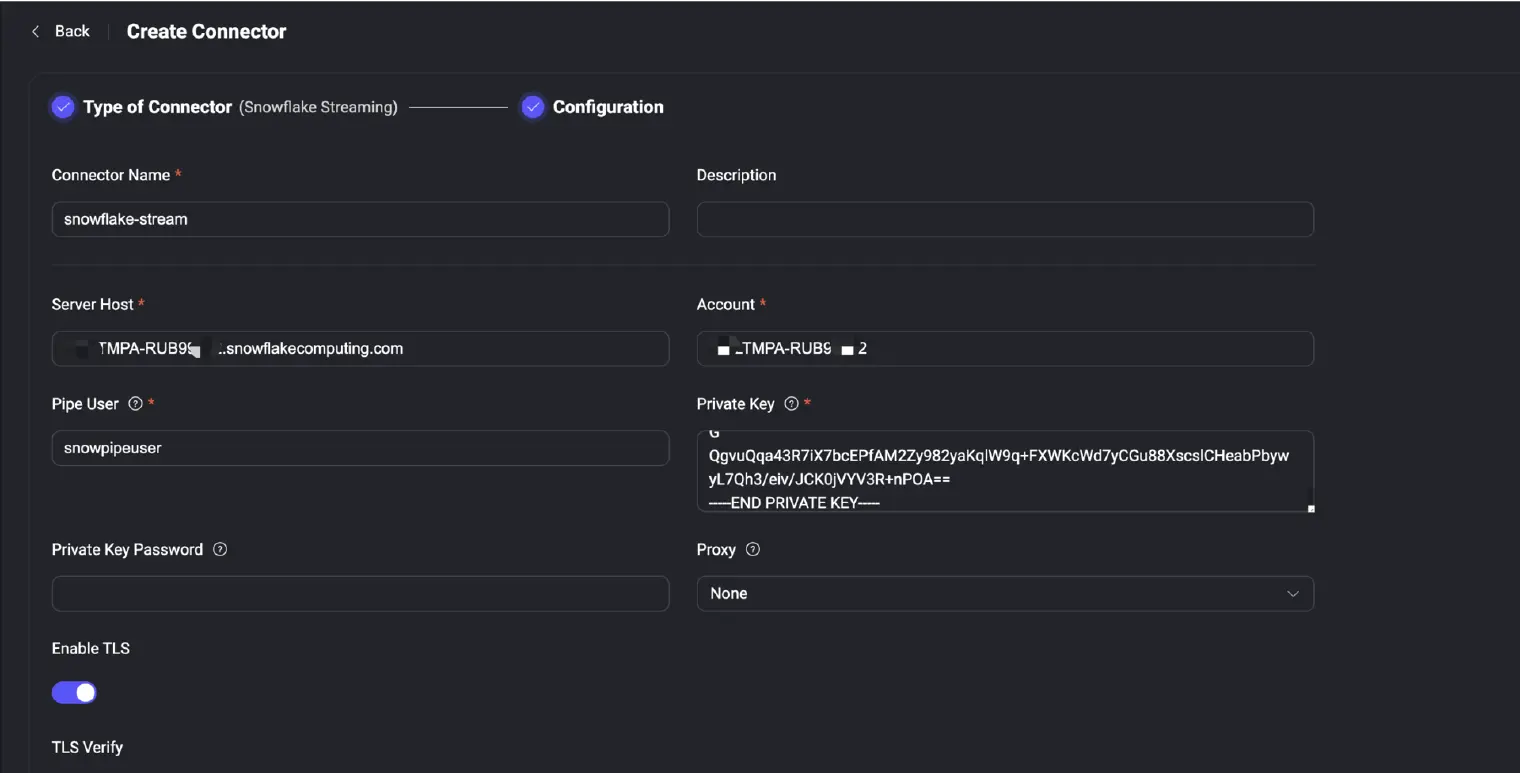
In the EMQX Dashboard, navigate to Integration -> Connector and select Snowflake Streaming.
Fill in the connection details:
- Server Host: Your Snowflake Account URL (e.g.,
TMPA-RUB95.snowflakecomputing.com) - Account: Your account identifier (e.g.,
{OrganizationName}-Account Name{}) - Pipe User:
snowpipeuser - Private Key: Paste the contents of your generated private key file
- Enable TLS: Must be enabled
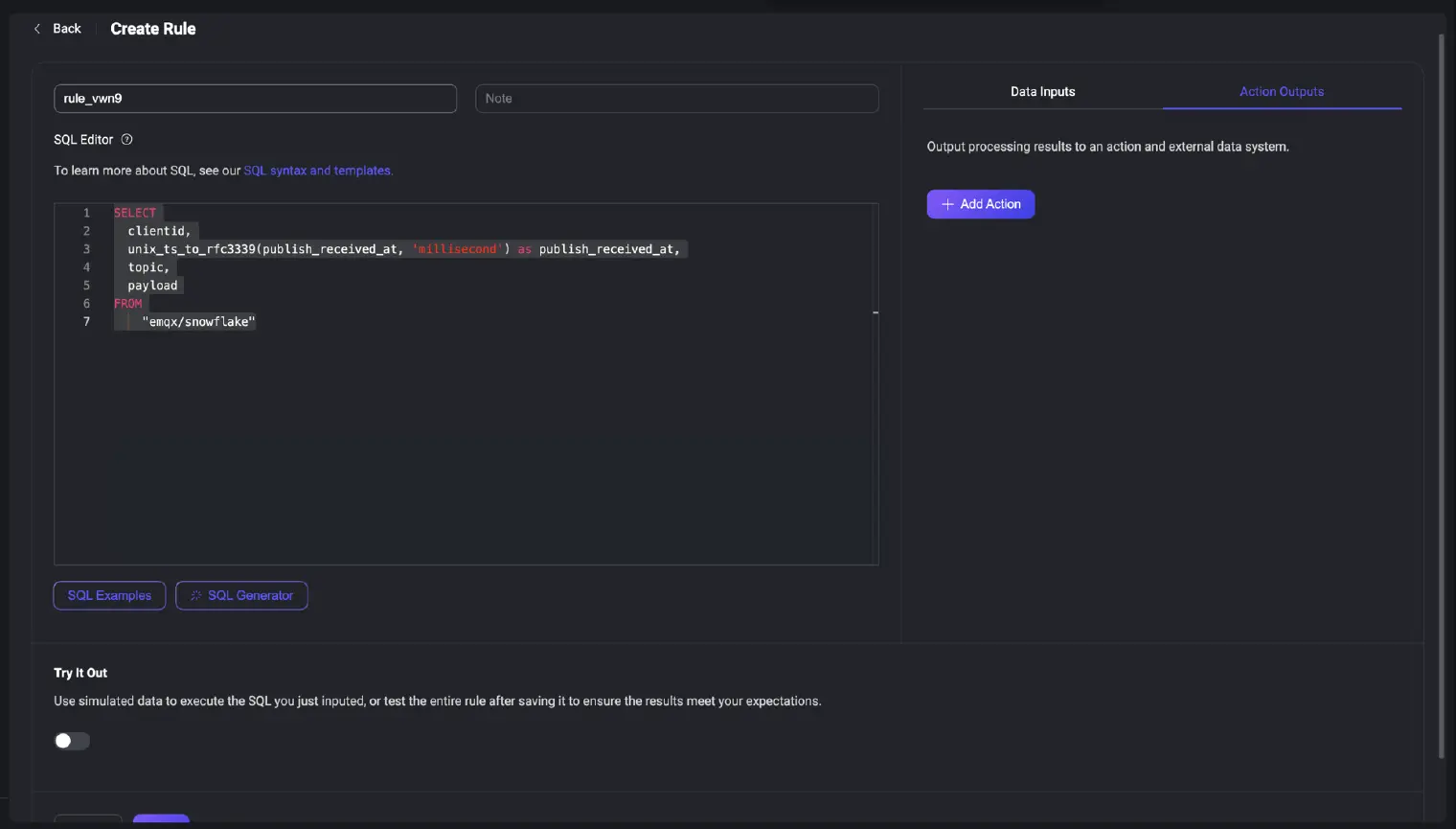
Step 2. Create a Rule to Process Data
Next, go to Integration -> Rules and create a new rule. The Rule's SQL defines which data to send.
Use this SQL to select messages from the emqx/snowflake topic and format the timestamp for Snowflake:
SELECT
clientid,
unix_ts_to_rfc3339(publish_received_at) as publish_received_at,
topic,
payload
FROM
"emqx/snowflake"
Step 3. Add the Action
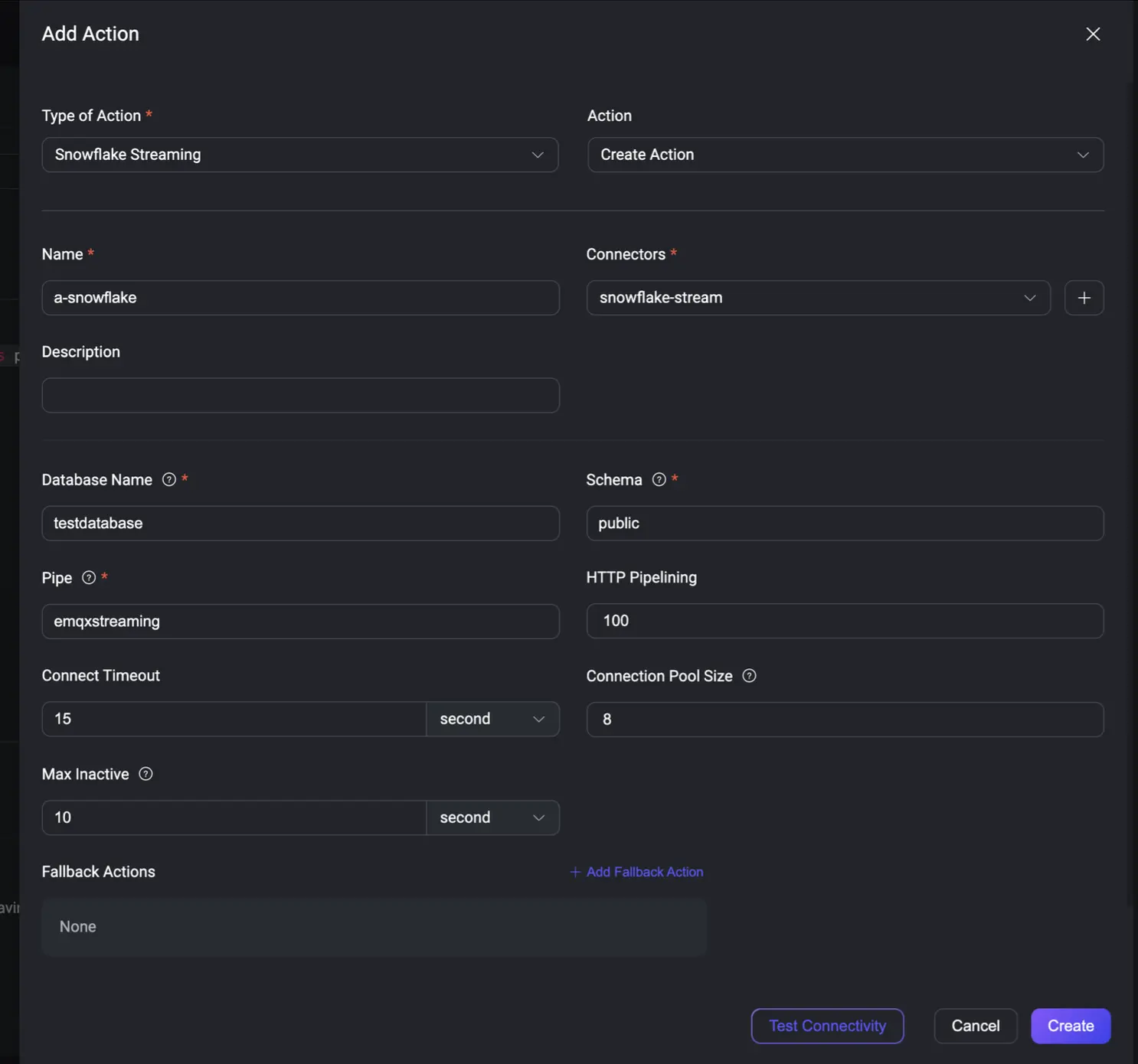
Click Add Action and select Snowflake Streaming.
- Connector: Choose the
snowflake-streamconnector you just created. - Database Name:
testdatabase - Schema:
public - Pipe:
emqxstreaming
Click Create, and you're done! The integration is now live.
Part 3: Test and Verify in Real Time
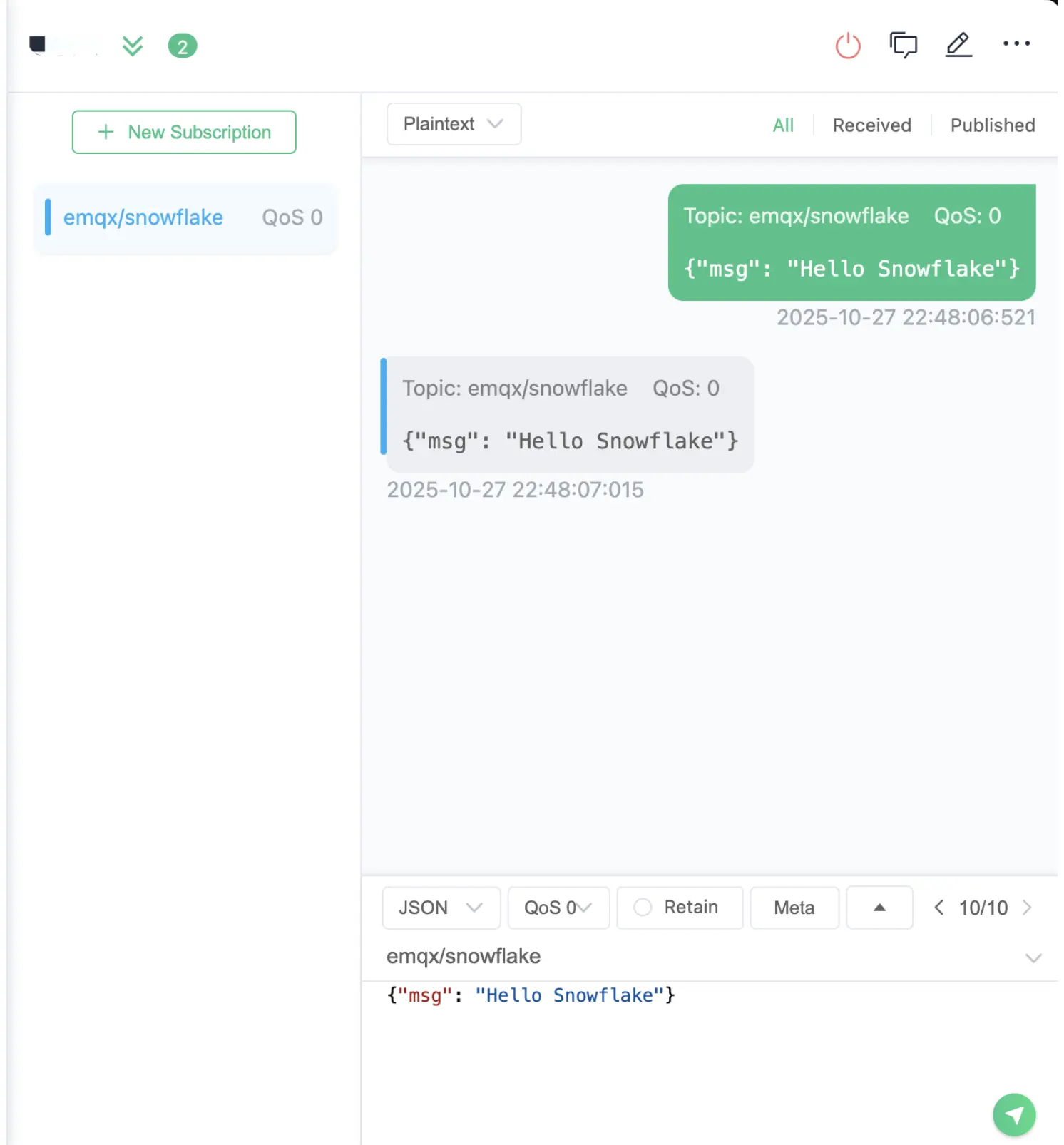
Step 1. Publish an MQTT Message
Use any MQTT client, like MQTTX, to publish a message to the topic you defined in the rule (emqx/snowflake).
- Topic:
emqx/snowflake - Payload:
{"msg": "Hello Snowflake"}
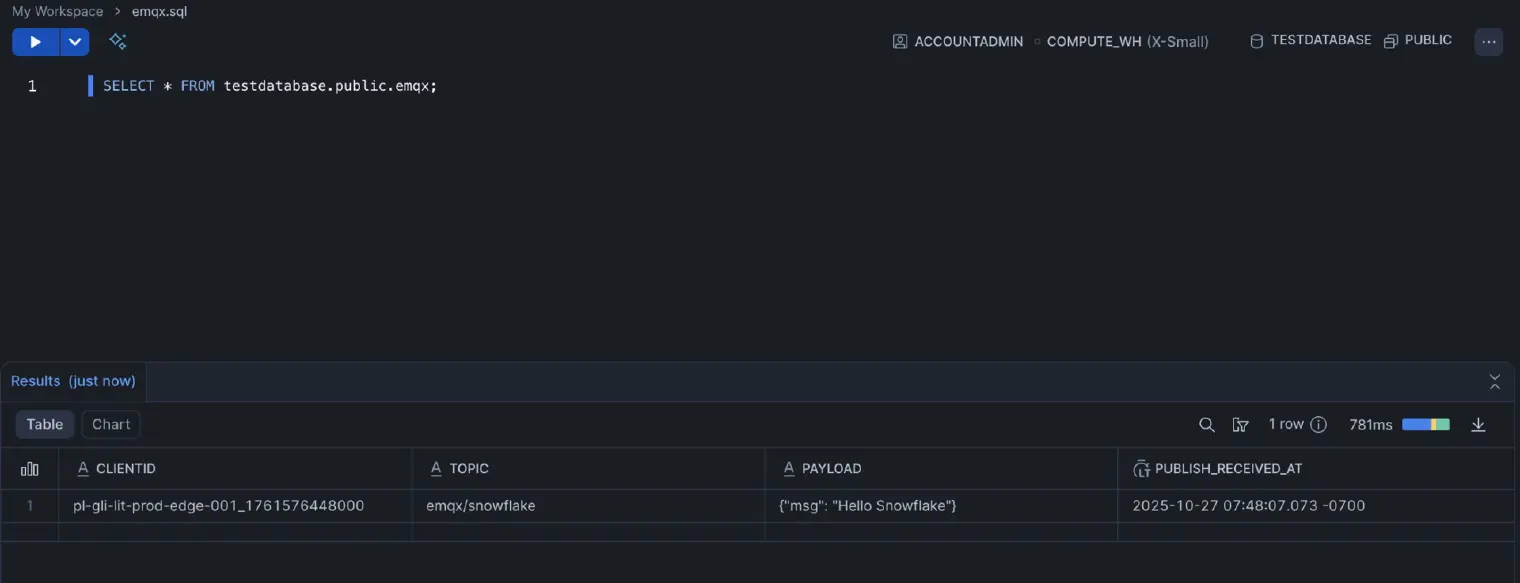
Step 2. See the Data in Snowflake Instantly
Head back to your Snowflake worksheet and query your table.
SELECT * FROM testdatabase.public.emqx;
Instantly, you'll see your test data. No batch jobs, no staging, no waiting.
Unlock Your Real-Time Data
In just a few simple steps, you have built a robust, real-time data pipeline from your IoT devices directly into Snowflake. Stop waiting for batch-processed data and start unlocking immediate insights from your IoT deployments with EMQX and Snowflake.
