From MQTT to Data Lakehouse: Building Time-Series Pipelines with S3 Tables

Table of Contents
Integrating MQTT data streams with AWS S3 Tables enables you to build a scalable and queryable time-series data lakehouse. This guide walks you through best practices for creating an end-to-end pipeline — from IoT data ingestion in EMQX to structured storage in an Iceberg-based S3 Table, ready for analytics via Athena.
Part 1. Prepare AWS S3 Tables Resources
Before setting up the integration in EMQX, you must first create the necessary storage resources in AWS S3 Tables.
Step 1. Create a Table Bucket
- Log in to the AWS Management Console and open the S3 service.
- In the left navigation pane, select Table buckets.
- Click Create table bucket, enter a bucket name (e.g.,
mybucket), and click Create table bucket. - Once created, click your bucket name to open the Tables view.
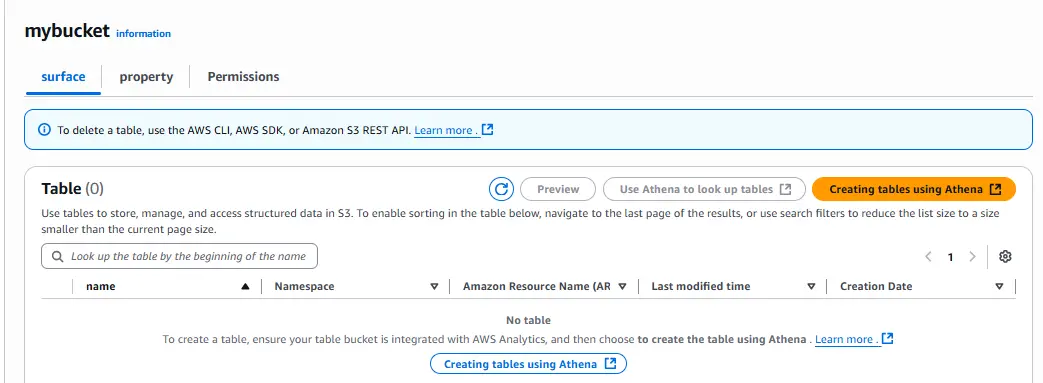
Step 2. Create a Namespace and Table
- Click Create table with Athena.
- When prompted for a namespace, click Create a namespace, provide a name (e.g.,
testns), and confirm. - Click Create table with Athena again.
Step 3.⚠️Complete Dual-Level Authorization (Database + Table)
AWS environment uses Lake Formation to manage the Glue Data Catalog, so you must grant both database-level and table-level permissions before creating or querying Iceberg tables in Athena.
1.Database-Level Authorization:
- Open Lake Formation Console → Data Catalog → Databases.
- Locate the namespace you just created (e.g.,
testns). - Click Actions - Grant permissions.
- In the pop-up window:
- Principals: Select your IAM user or role (⚠️ The Root account cannot be granted any permissions).
- Database: Choose the corresponding namespace (e.g.,
testns). - Permissions: Check Super and Grantable Super.
- Click Grant to save the authorization.
- Return to the Athena Query Editor and re-run the CREATE TABLE statement — it should now execute successfully.
2. Table-Level Authorization:
After the table is created, grant the same Super permissions at the table level:
- In Lake Formation → Data Catalog → Tables, locate the newly created table (e.g.,
testtable). - Click Actions → Grant permissions.
- Add the same IAM user or role.
- Check Super and Grantable Super.
- Click Grant to complete the authorization.
Once both database-level and table-level permissions are granted, your IAM user can fully create, query, and manage Iceberg tables in Athena.
Step 4. Verify IAM User Policies
Before using Athena and Lake Formation together, make sure your IAM user (for example, emqx-s3tables-user) has all required policies attached.
These permissions allow the user to manage S3 Tables, create Iceberg tables, and grant Lake Formation access without restriction.
Required IAM Policies:
| Service | Policy Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| IAM | AdministratorAccess (optional but recommended for testing) |
Full administrative privileges for setup and debugging |
| Amazon Athena | AmazonAthenaFullAccess |
Allows query and table creation in Athena |
| Amazon S3 | AmazonS3FullAccess |
Enables read/write access to S3 buckets and objects |
| S3 Tables | AmazonS3TablesLakeFormationServiceRole |
Required for S3 Tables integration with Lake Formation |
| Glue | AWSGlueConsoleFullAccess |
Enables database and table operations in Glue Data Catalog |
| Lake Formation | AWSLakeFormationDataAdmin |
Grants management access for database/table permissions |
| Cross-account | AWSLakeFormationCrossAccountManager |
For managing cross-account permissions if needed |
In the AWS IAM console, the Permissions tab of emqx-s3tables-user should list policies similar to:
AdministratorAccess
AmazonAthenaFullAccess
AmazonS3FullAccess
AmazonS3TablesLakeFormationServiceRole
AWSGlueConsoleFullAccess
AWSLakeFormationDataAdmin
LakeFormationAdminCustom
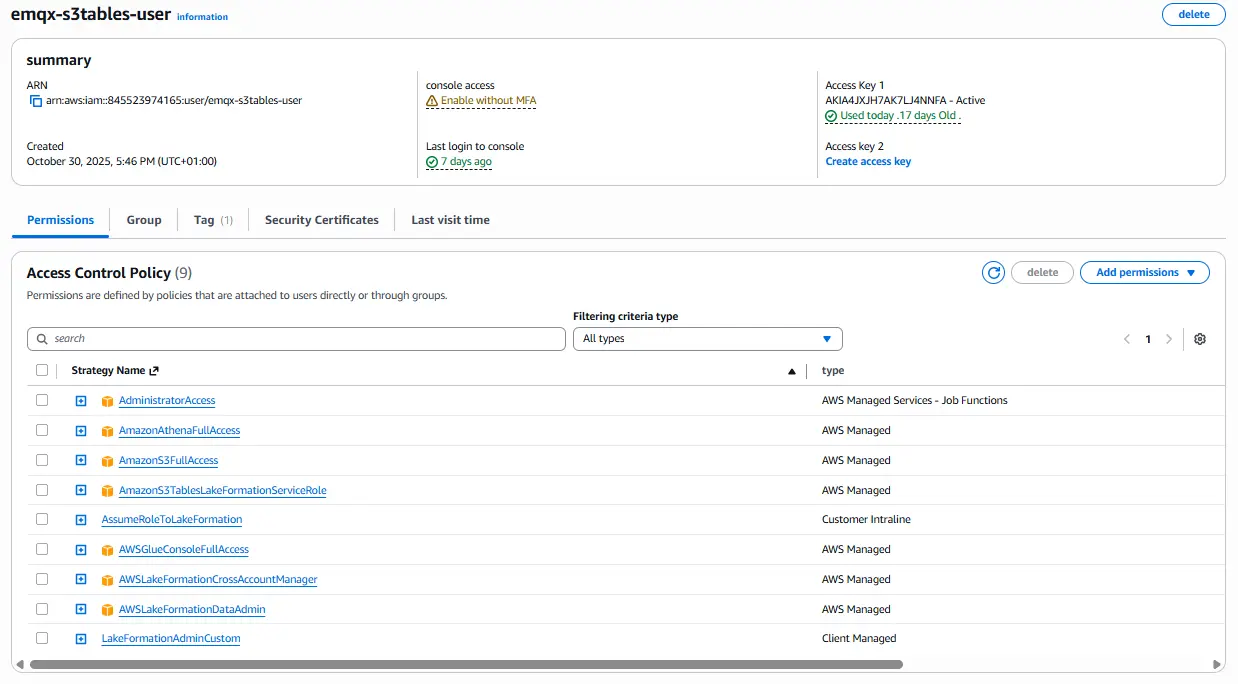
Ensuring your IAM user has these policies, combined with Lake Formation database and table-level “Super” permissions, will prevent all common access errors when integrating EMQX with AWS S3 Tables and Athena.
Step 5. Verify the Table in Athena
Open the Query table with Athena, then select your Catalog (e.g.,
s3tablescatalog/mybucket) and your newly created namespace.Run the following DDL to create an Iceberg table:
CREATE TABLE `testns`.testtable ( clientid string, topic string, payload string, publish_received_at timestamp ) TBLPROPERTIES ('table_type' = 'iceberg');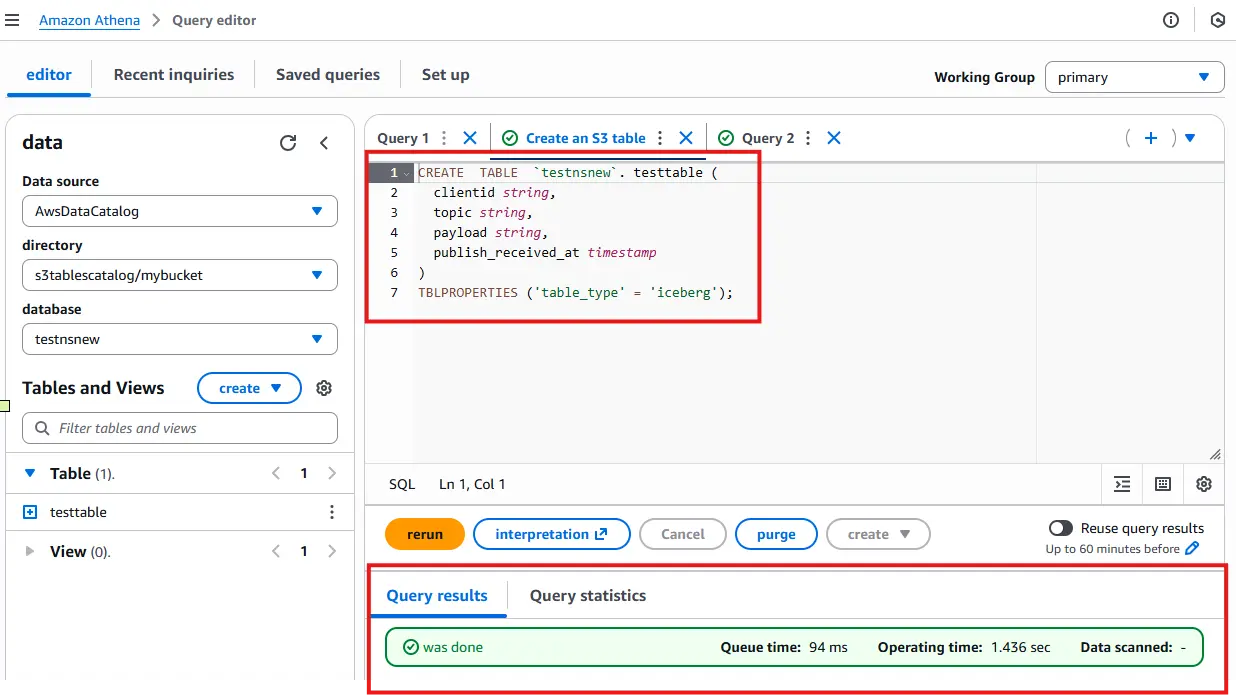
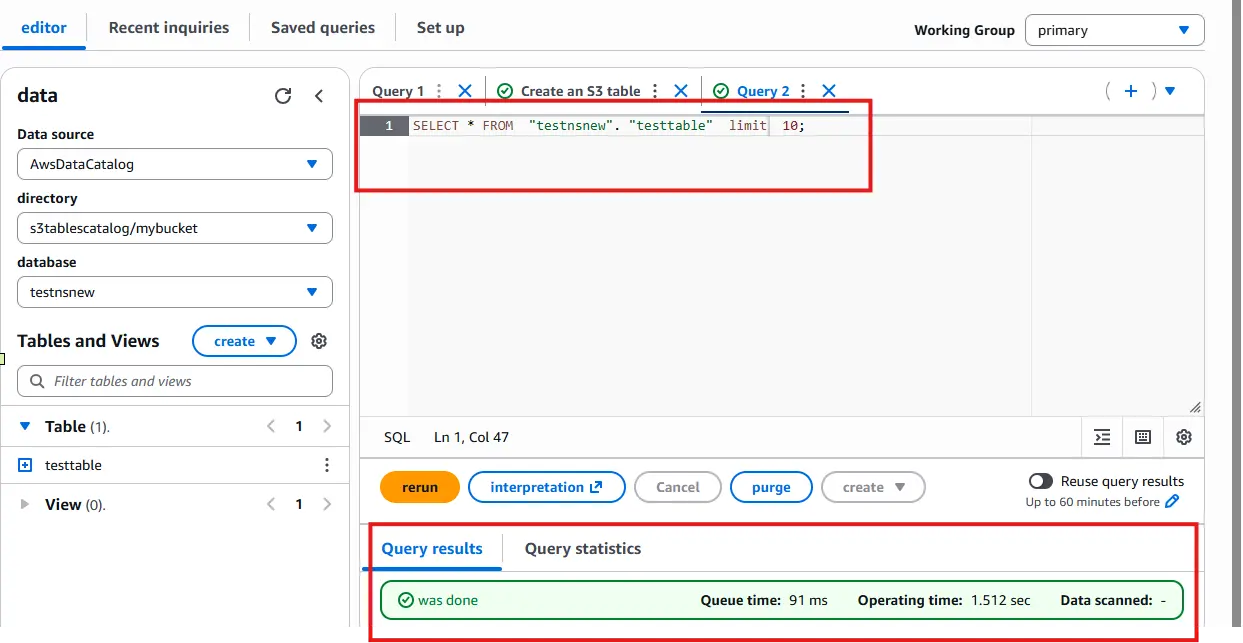
Verify the table creation:
SELECT * FROM testtable;
If the query returns no rows, your table is successfully initialized and ready to receive MQTT data.
Part 2. Configure S3 Tables Integration in EMQX
Now that your destination is ready, you can configure EMQX to stream MQTT data into S3 Tables.
Step 1. Create a Connector
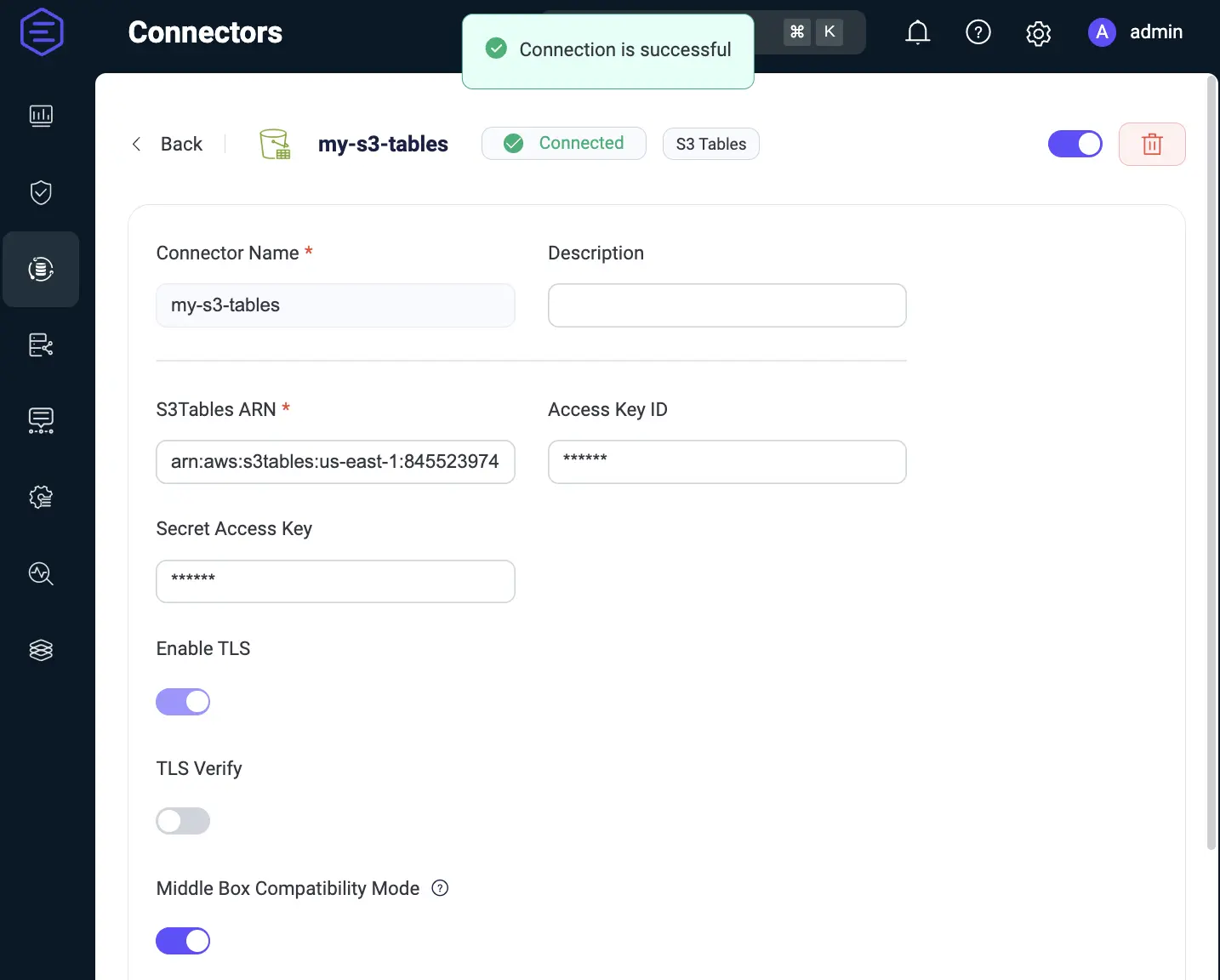
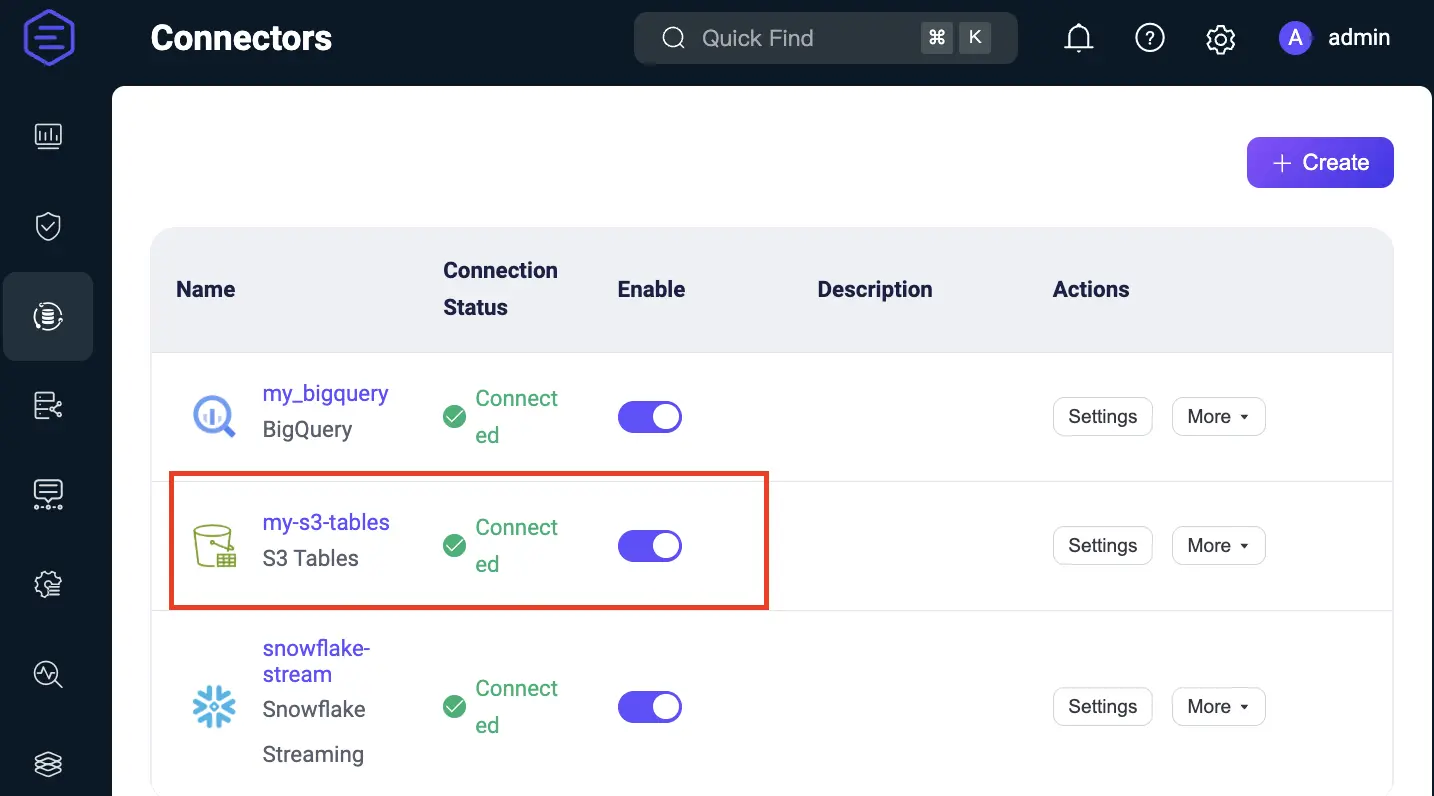
Step 2. Create Rule and Action
Go to Integration → Rules, click Create.
Enter rule ID:
my_rule.In the SQL editor, add:
SELECT clientid, topic, payload, publish_received_at * 1000 AS publish_received_at FROM "t/s3t"Tip: Ensure the output fields exactly match your Iceberg table schema. A mismatch may prevent data from being written.
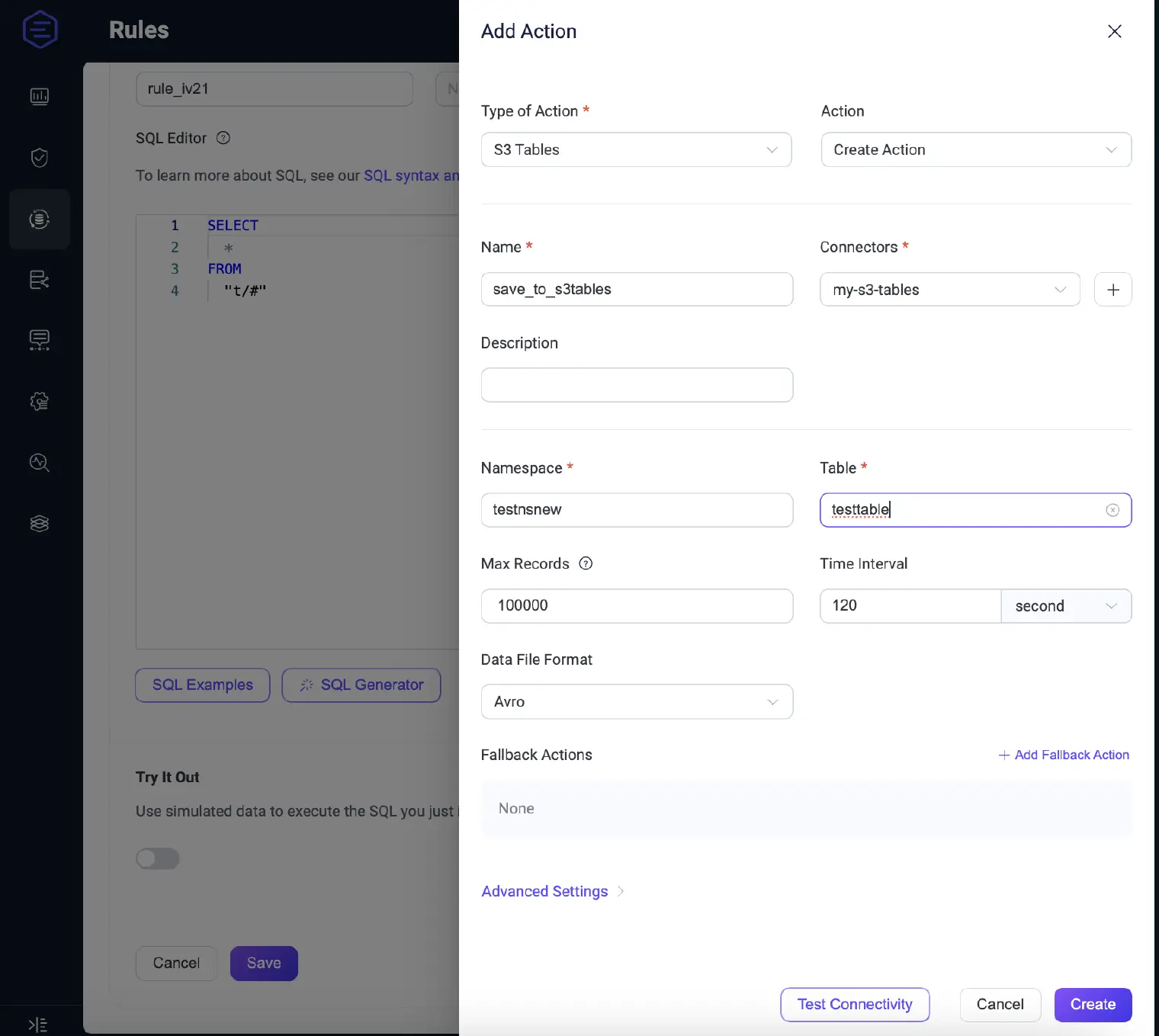
Under Actions, select S3 Tables from the Action Type dropdown and click Create new action.
Configure the action:
- Name: e.g.,
to_s3tables_action - Connector: Select the
my-s3-tablesconnector created earlier - Namespace: e.g.,
testns - Table: e.g.,
testtable - Max Records: e.g.,
500 - Time Interval: e.g.,
5000(milliseconds) - Data File Format: choose between
avro(default) orparquet
- Name: e.g.,
Click Create to save the action, then Create again to finalize the rule.
Part 3. Test the Pipeline
Now use the MQTTX Client to publish a test message and trigger the pipeline.
Open the MQTTX application and connect to your EMQX broker.
- Client ID:
emqx_c - Topic:
t/s3t - QoS:
0
- Client ID:
In the message field, enter:
"Bonjour S3 Tables"Click Publish to send the message.
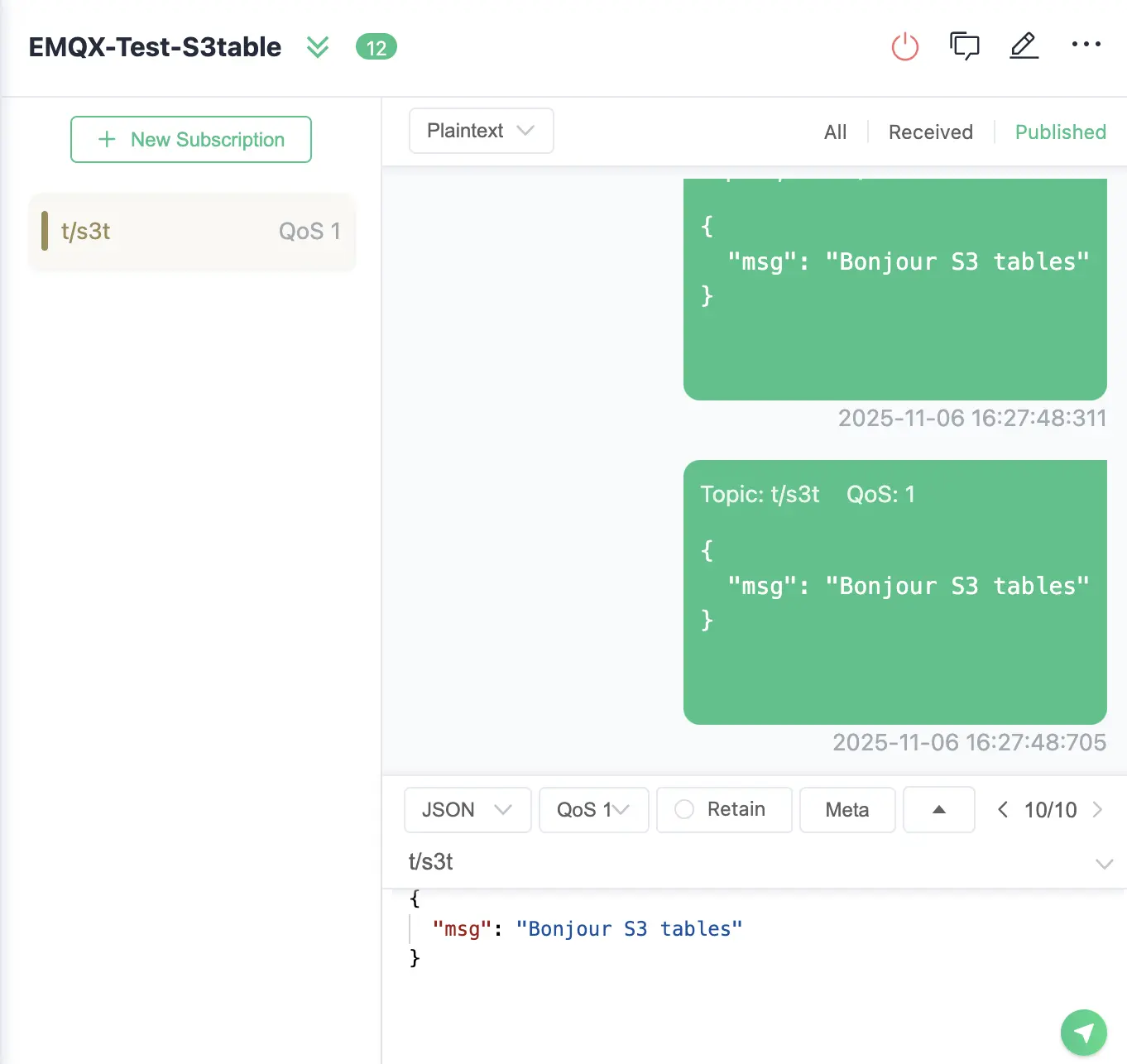
This message will be processed by EMQX according to the defined rule and written to your S3 Tables destination.
Part 4. Verify Data in Athena
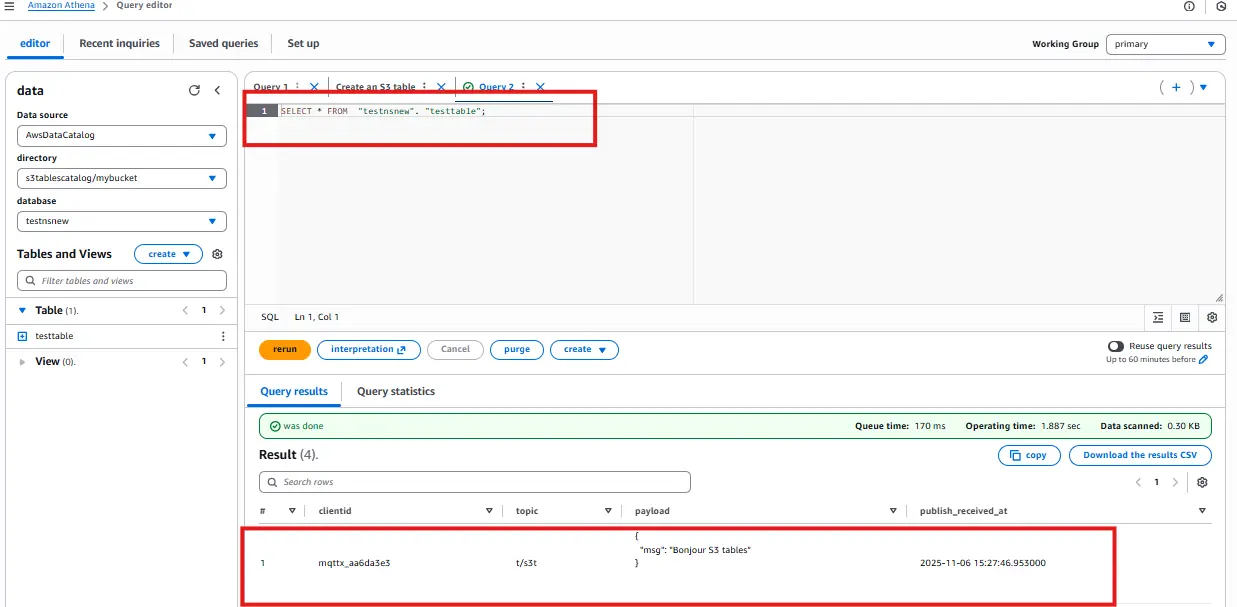
Go back to Athena Query Editor and run:
SELECT * FROM testtable;
You should now see your MQTT message (“Hello S3 Tables”) appear as a record in your Iceberg table.
Conclusion
You have now built a complete time-series data pipeline — streaming MQTT messages from EMQX into AWS S3 Tables as structured Iceberg datasets.
This setup bridges IoT and big data analytics, enabling powerful querying and time-series analysis directly in your data lakehouse.
