Connecting to the Modern Data Lakehouse: Streaming IoT Data to Snowflake, BigQuery, and S3 Tables

Table of Contents
- The Challenge of Real-Time IoT Data
- EMQX 6.0: Bridging the Data-to-Insight Gap with Expanded Data Integrations
- Spotlight Integrations: Snowflake, BigQuery, and S3 Tables
- Real-Time Streaming to Snowflake
- Seamless Ingestion to Google BigQuery
- Structured Persistence with S3 Tables
- Conclusion: From Data Silos to Data Lakehouse, Natively
The Challenge of Real-Time IoT Data
IoT data is the new fuel for enterprises and AI, but processing it is highly challenging.
The core hurdles enterprises face in moving high-volume, real-time IoT data from the edge to analytics systems include:
- Velocity and Volume: Managing continuous, high-speed streams from millions of devices, not traditional batch uploads.
- Latency of Insight: Traditional analytics are too slow; a critical machine failure detected in the data must be acted upon in seconds, not hours.
- Data Heterogeneity: Dealing with diverse, imperfect data formats (JSON, Avro, raw binary) that require filtering and normalization.
- OT System Strain: Legacy synchronous polling methods designed for Operational Technology (OT) systems can dangerously impact the performance and reliability of source control systems (like PLCs).
The clear solution is a decoupled, event-driven architecture that can ingest data once and reliably deliver it to multiple analytical consumers without impacting the source.
EMQX 6.0: Bridging the Data-to-Insight Gap with Expanded Data Integrations
EMQX 6.0 has transformed from an MQTT broker into a unified platform for all IoT data movement. The enhanced Data Integration framework features an integrated, SQL-driven engine to seamlessly process and route high-volume edge data directly into the modern data lakehouse. This makes real-time insight an out-of-the-box feature.
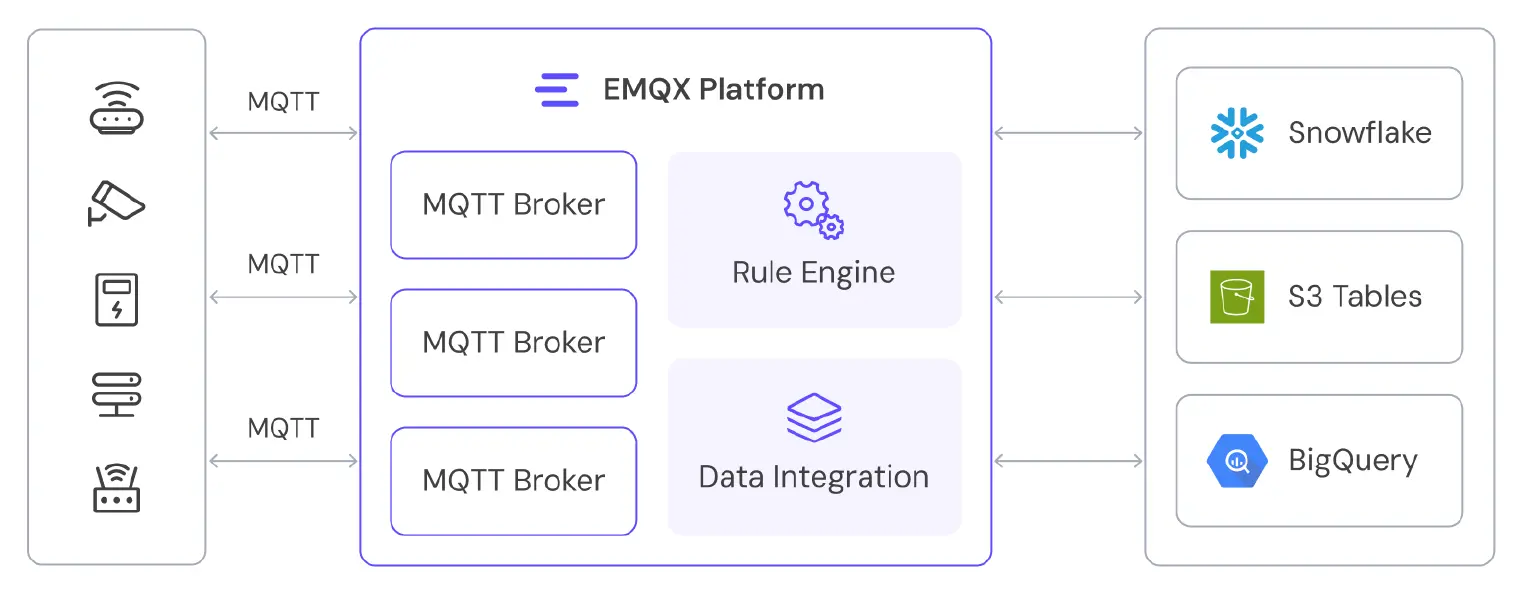
Modern Data Lakehouse Destinations in EMQX 6.0:
| Destination | Platform Type | EMQX 6.0 Integration | Ingestion Method | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Snowflake | Cloud Data Warehouse | Enhanced | Snowpipe Streaming | Near-Real-Time Latency (seconds, no staging) |
| Google BigQuery | Serverless Analytics | New | Native API Streaming | Petabyte-Scale & AI-Readiness (native ML) |
| S3 Tables | Open Data Lakehouse | Enhanced | Apache Iceberg Format | Openness & Decoupling (queryable by any engine) |
| AWS Redshift | Cloud Data Warehouse | New | Native API Streaming | Scalable, high-performance columnar analytics |
| AWS AlloyDB | Operational Database | New | Native Connection | High-performance, PostgreSQL-compatible transactional analytics |
| CockroachDB | Distributed SQL DB | New | Native Connection | Planet-scale data resiliency and geo-distribution |
| RabbitMQ Sink | Message Queue | Enhanced | Header/Property Templates | Enhanced message routing and compatibility within RabbitMQ |
Spotlight Integrations: Snowflake, BigQuery, and S3 Tables
This post will focus on three critical and optimized cloud integrations that cover the dominant paradigms of modern data analytics:
- Snowflake Streaming (New): Leveraging the low-latency Snowpipe Streaming feature for a real-time cloud data warehouse experience.
- Google BigQuery (New): A brand-new, native connector for high-volume, infinitely scalable serverless analytics and AI platforms.
- S3 Tables (Enhanced): Structured data persistence directly to Apache Iceberg tables, forming the foundation of a flexible, vendor-agnostic data lakehouse.
EMQX 6.0 provides specific, optimized, and native pathways to all major cloud data architectures, allowing your organization to use a single, unified ingestion platform to feed all its downstream data strategies—from real-time operational visibility to large-scale AI modeling and low-cost archival.
Real-Time Streaming to Snowflake
The EMQX integration with Snowflake enables IoT data to be written directly to Snowflake tables for analytics, data archiving, and integration with other business processes. The game-changing enhancement in EMQX 6.0 is the support for Snowpipe Streaming. This new ingestion method, currently in preview, is designed for low-latency streaming and fundamentally changes Snowflake's viability for real-time IoT use cases.
Why Snowpipe Streaming Matters
- Ultra-Fast Data Availability: Data availability shifts from minutes or hours to seconds, providing near-instant access for query and analysis and fundamentally moving past traditional batch processing.
- Simplified Architecture & Cost Efficiency: Snowpipe Streaming removes traditional steps like buffering data, uploading to S3, and running
COPY INTOjobs. By writing data directly from EMQX into Snowflake tables, this integration eliminates intermediate storage, reduces management overhead, and lowers costs associated with micro-batching and file handling. - Real-Time IoT Enablement: This direct streaming capability transforms Snowflake from a purely analytical data warehouse into a near-real-time operational platform, making it a streamlined, cost-effective choice for IoT data processing.
Use Case: Live Dashboards for Industrial IoT (IIoT)
- Scenario: A manufacturing plant manager requires a live dashboard to monitor Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) and critical sensor thresholds, such as a reactor's temperature or pressure.
- Implementation: Data from on-floor PLCs and sensors is published via MQTT to EMQX. The EMQX rule engine processes and routes this data through the Snowpipe Streaming Sink.
- Business Value: The data lands in Snowflake within seconds and is immediately queryable by the manager's live dashboard (e.g., in Tableau or Power BI). This enables on-the-fly anomaly detection, flagging a sensor reading the moment it exceeds a safety threshold, rather than waiting for an end-of-shift batch report. This facilitates proactive maintenance, prevents costly downtime, and improves worker safety.
Seamless Ingestion to Google BigQuery
Google BigQuery is a fully managed, serverless, petabyte-scale enterprise data warehouse optimized for large-scale, ad-hoc SQL-based analysis. EMQX 6.0’s native data integration for BigQuery allows massive IoT datasets to be streamed directly into BigQuery, making them immediately available for advanced querying and machine learning.
The Value of EMQX's Native BigQuery Connector
- Direct, Simplified Architecture: EMQX now streams IoT data directly into BigQuery, eliminating the need for Pub/Sub and Dataflow. This streamlined pipeline, Device → EMQX → BigQuery, cuts latency, cost, and configuration overhead. It acts as the "easy button" that fills the gap left by the discontinuation of Google's own IoT Core.
- Clean, Analytics-Ready Data: Data is ingested directly into BigQuery's fully managed, petabyte-scale, serverless architecture. The EMQX rule engine supports real-time data transformation, filtering, and enrichment, ensuring that only clean, structured data reaches BigQuery.
- Access to the Google Cloud AI/ML Ecosystem: Once ingested, data becomes instantly available across the Google Cloud AI/ML ecosystem—including Vertex AI, Looker, and Data Studio—empowering enterprises to easily build, train, and deploy AI models using fresh IoT data.
Use Case: Connected Vehicle Data for Predictive Maintenance
- Scenario: An automotive manufacturer collects real-time telemetry (CAN bus data, GPS location, battery charge/discharge cycles) from millions of connected electric vehicles. The goal is to train machine learning models to predict battery degradation and identify component failure patterns before they occur.
- Implementation: EMQX serves as the global ingestion hub, supporting millions of concurrent MQTT connections from the vehicle fleet. The new BigQuery Sink streams this continuous, petabyte-scale dataset directly into BigQuery tables.
- Business Value: Data science teams can use BigQuery ML to run and train predictive models directly on the raw, real-time telemetry data. This "drives updates to intelligent driving algorithm models", enabling the company to send proactive maintenance alerts to drivers ("Your battery shows 8% degradation, schedule service") and feed R&D for future battery designs.
Structured Persistence with S3 Tables
This final integration is strategically different from the first two. It is not about writing data into a proprietary database; it is about writing data into open-format tables built on ubiquitous object storage. EMQX 6.0's enhanced S3 Tables connector writes MQTT messages directly into tables formatted as Apache Iceberg, a high-performance, open table format purpose-built for massive-scale analytics workloads.
Why This Integration is Strategic
- Storage–Compute Decoupling for Cost Efficiency: IoT data is stored in open formats like Iceberg or Parquet on low-cost, scalable object storage (S3). Analytics engines such as Amazon Athena can then query the data on demand—eliminating the need for always-on compute and dramatically reducing long-term costs for massive datasets like smart meter readings.
- Freedom from Vendor Lock-In: Unlike Snowflake or BigQuery, which store data in proprietary formats, the S3 Tables connector writes to open standards. This ensures full data ownership and flexibility to use multiple analytics engines across different ecosystems.
- One Data Source, Unlimited Insights: By writing data to the open Iceberg standard once, an organization can empower multiple teams to use their preferred analytics tools on the same single source of truth, from Amazon services (Athena, Redshift, EMR) to third-party engines (Snowflake, Presto, or Trino). This realizes the Data Lakehouse principle with flexibility and open integration.
Use Case: Smart Grid Data for Long-Term Archival and Analytics
- Scenario: A utility company must collect and store decades of smart meter readings from millions of homes and businesses for regulatory compliance, billing validation, and long-term energy grid analysis.
- Implementation: Millions of smart meters publish their interval readings to EMQX. The
S3 TablesSink is configured to process this data and write it into partitioned Apache Iceberg tables (e.g., partitioned byyear,month, andday) using theparquetformat. - Business Value: The data is stored durably and at an extremely low cost on Amazon S3 for compliance and archival. When analysts need to run a complex historical query (e.g., "Analyze peak load in July for the last 10 years"), they can use Amazon Athena. Because the data is in Parquet (columnar) and partitioned by date, the query engine only reads the exact data required, delivering high performance without the high cost of keeping 10 years of data "hot" in a traditional data warehouse.
Conclusion: From Data Silos to Data Lakehouse, Natively
EMQX 6.0's enhanced data integration framework serves as the critical accelerator for IoT's adoption of the modern data paradigm. It closes the gap from edge to insight, making real-time, AI-ready analytics an out-of-the-box capability rather than a multi-year, custom-engineering project.
See it in action — Try EMQX 6.0 and start streaming IoT data to Snowflake, BigQuery, or S3 for real-time, AI-ready insights today!
